What is ARR?
ARR meaning
Annual Recurring Revenue, commonly referred to as ARR, is the annual version of Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and is the total revenue a company expects to earn from its customers annually through its subscription services. ARR is a SaaS KPI (key performance indicator) for businesses that rely on subscription models, as it helps in forecasting long-term revenue and assessing the company's financial health.
Why is ARR Important?
Tracking your ARR finance as well as MRR is a must for any subscription business. ARR serves as a cornerstone for strategic decision-making in subscription-based businesses. Here's why ARR is essential:
- Predictable Revenue Streams: ARR provides a clear view of the recurring revenue, allowing businesses to plan and allocate resources more effectively.
- Investor Confidence: Investors often look at ARR to gauge a company's stability and growth potential. A steady or growing ARR indicates a healthy, sustainable business.
- Performance Measurement: ARR helps in measuring the success of subscription strategies and customer retention efforts, highlighting areas for improvement.
Calculating ARR
Understanding how to calculate ARR is crucial for accurate financial forecasting. The basic formula for ARR is:
ARR = (Monthly Recurring Revenue) × 12 months
For instance, if a company has 1,000 customers, each paying $1,200 per year, the ARR would be:
ARR = 1,000 customers × $1,200 per customers = $1,200,000
It is important to remember that ARR does not include non-recurring revenue such as: one-off charges, set-up fees, non-recurring add-ons and so on.
ARR vs. MRR vs. Revenue
While ARR focuses on annual revenue, Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) provides insights into the revenue generated on a monthly basis. Both metrics are crucial, but they serve different purposes:
- MRR: Is your potential earnings every month and is useful for short-term planning and tracking monthly growth trends. It's particularly helpful for identifying immediate issues or opportunities.
- ARR: Is your potential earnings every year and provides a long-term perspective, helping in strategic planning and long-term financial health assessment.
- Total Revenue: Is your realized earnings in a given period.
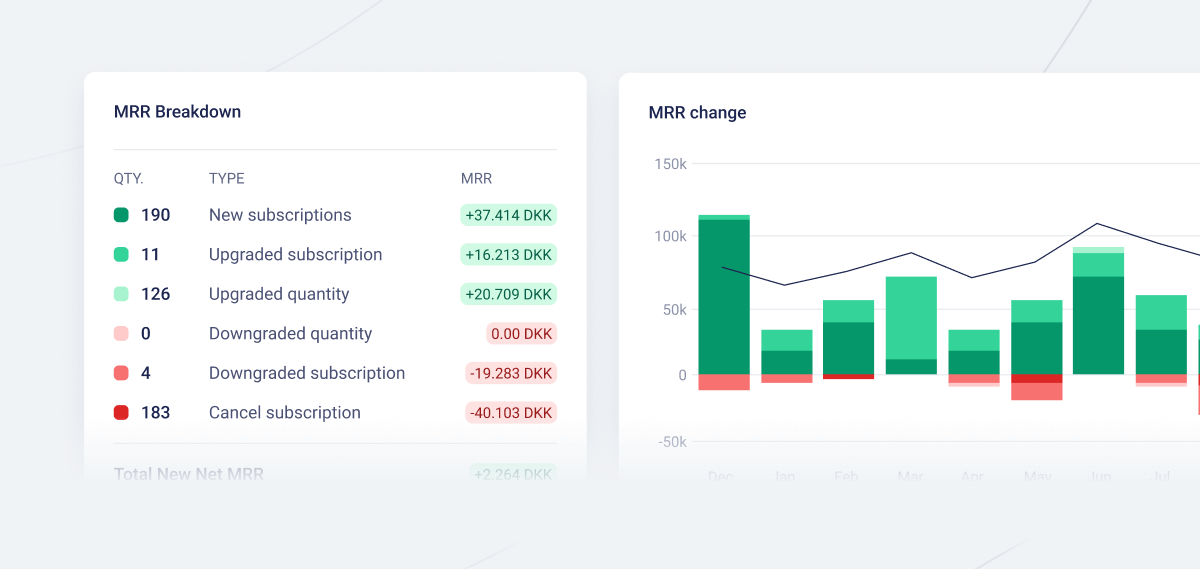 Fenerum dashboard showing SaaS MRR and MRR Breakdown.
Fenerum dashboard showing SaaS MRR and MRR Breakdown.
Enhancing ARR with Subscription Management
Effective subscription management is critical to maximizing ARR. Here are some strategies to boost ARR through better subscription management:
Customer Retention
Implementing loyalty programs and providing exceptional customer service can reduce churn-rates, thereby increasing ARR.
Upselling and Cross-Selling
Offering additional products or premium features to existing customers can increase the average revenue per customer.
Pricing Strategies
Regularly reviewing and adjusting pricing models ensures the business remains competitive and profitable.
Some popular B2B subscription management tools in 2024 ncludes Fenerum, Stripe Billingand Younium.
Conclusion
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is more than just a SaaS metric; it's a comprehensive indicator of a company's financial health and growth potential. By understanding and leveraging ARR, businesses can make informed decisions, foster investor confidence, and enhance their subscription management strategies. Tracking your ARR is a must if you want to survive in today's fast-pace world og subscription metrics and KPIs.
